Archive for May, 2013
Information on swelling in stomach lymph node
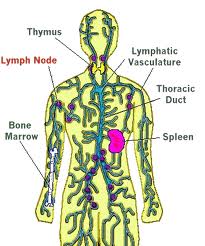
Lymph nodes are bean-shaped glands that are found throughout the human body. They are a part of the lymphatic system that caries nutrients, fluids and toxins between the bloodstream and the tissues. Having a strong lymphatic system is important if you want to protect your body from diseases. The main function of the lymph nodes is to trap and destroy the viruses and bacteria using lymphocytes.
Where can you find lymph nodes?
These nodes are found either singly or in small groups. The size of the lymph nodes vary depending on the function they have to perform. Some lymph nodes are as small as size of the head of a pin while others are as large as an olive. You can feel groups of lymph nodes in the underarms and the neck. You can also find lymph nodes in the abdomen close to the internal organs.
How do lymph nodes get swollen?
The lymph nodes of the body are usually not painful and cannot be felt. However, you could feel some pain when they swell. This swelling is caused by an infection, tumor or injury. If the lymph nodes swell in at least two areas, it is called lymphadenopathy. The main causes of lymphadenopathy include:
- Bacterial Infection
- Viral Illness
- Cancer
Diagnosis of swelling in abdominal lymph nodes
Since the lymph nodes of the abdomen are too small to be felt in a normal examination, your doctor could suggest a CT scan or sonography to examine the condition of the lymph nodes. You may also have to undergo a few other tests like endoscopic examination and blood tests to find out the cause of lymph node enlargement. There are many diseases that can enlarge the lymph nodes and it is difficult to known the disease which causes the swelling. Your doctor could do a biopsy (take a small sample) to find out the disease that is causing the problem. The treatment will start only after the doctor completes the biopsy.
How is the biopsy done?
If the patient is not only suffering from swelling in the abdominal lymph nodes but also in the lymph nodes of the groins or armpits, the doctor may take a small sample from these areas. These samples are then sent to pathologist for examination. To extract a sample from the lymph nodes, the patient is either given local or general anaesthesia.
The situation is different for patients who have swelling only in the lymph nodes of the abdomen. In such situations, the doctor may do biopsy of lymph nodes of the abdominal region using CT scan or ultrasound. The doctor is likely to pass a needle to the area of swell and take a small sample to find out the bacteria or virus that is causing the swelling.
What happens if the biopsy does not yield any result?
At times, the sample taken by the doctor is too small, which could make it difficult for the pathologist to give a correct diagnosis of the cause of the problem. Also, in some patients the lymph node is located close to an important or sensitive internal organ, which can make it risky for the doctor to conduct a biopsy. Traditionally these patients would have had to undergo a small operation so a sample is obtained from the enlarged lymph node. Today, since lymph nodes of the abdominal regional cannot be biopsied using CT scans, most doctors use laparoscopic biopsy to obtain a sample from the lymph node.
How is laparoscopic biopsy performed?
Laparoscopic biopsy is usually carried out after the patient is given general anaesthesia. The surgeon makes a small cut and inserts tube called cannula in the affected area of the abdomen. The tubes are connected to a special pump that pumps in carbon dioxide gas. When the abdomen gets filled with carbon dioxide gas, it is lifted up which makes it easy for the surgeon to extract sample from the lymph node.
The cannula is then disconnected from the pump and telescope that is connected to a video camera is passed through the cannula. The telescope transmits the images of the lymph node to the television screen. The surgeon then gets the biopsy of the lymph node by inserting a long instrument through the cannula. The surgeon sends the sample the pathologist immediately to check its adequacy. If the sample is inadequate, the surgeon can more sample before completing the operation. The analysis of the sample can take up to 7 days because several tests are conducted on the sample.
Benefits of laparoscopic biopsy over traditional biopsy
Some of the benefits that laparoscopic biopsy has over traditional biopsy are:
- Less pain from incisions
- Faster return to work and normal diet
- Ability to get samples from sensitive areas
- Shorter stay at the hospital
- Shorter recovery time
How overeating affects your body
 It is difficult to find people who havenât dealt with problem of overeating. Before you start considering overeating as a problem, you must understand how overeating effects your body and the steps you can take to prevent overeating.
It is difficult to find people who havenât dealt with problem of overeating. Before you start considering overeating as a problem, you must understand how overeating effects your body and the steps you can take to prevent overeating.
Occasional overeating at social gatherings may not adversely affect your body. For instance, if you go to an office party and are unable to control your temptation to eat delicious food it may not adversely affect your body. If you overeat occasionally, you can take steps to control the temporary side effects of overeating. However, if you overeat regularly it can damage your body in the long run. Weight gain and additional fat deposit caused due to overeating can cause long-term weight gain.
Overeating and Dopamine Levels
Studies have shown that most people overeat because of a chemical compound called Dopamine. This chemical which is found in the human brain, induces a feeling of happiness when we eat. However, when we overeat the dopamine levels in the brain get depleted. When the dopamine levels get depleted, a person will have to eat more food to get a feeling of satisfaction.
However, overeating regularly can cause real damage in the long run. You gain extra calories and additional fat gets deposit in the body. Recent studies show that even one-month of overeating can lead to long-term weight gain.
Affect of Overeating on Stomach
To understand the impact of overeating on stomach, you must first understand how the stomach processes the food you eat. The food we eat gets stored in the upper part of the stomach which slowly gets transferred to the lower part of stomach for digestion. The strong muscles of stomach mash the food we eat and push it to small intestine.
When we overeat, the muscles in the stomach get stretched and ballooned up. If we overeat occasionally, we experience discomfort when the stomach muscles stretches. However, when we overeat regularly, we get used to this expansion and contraction of stomach muscles and no longer experience discomfort.
Another problem that people face when they overeat is that the digestive enzymes are available in limited quantity and they take time to digest bulk food. This can slow down the digestive process and the food we eat remains in the stomach for longer duration. This fullness of the stomach can sometimes cause discomfort, pain and misery.
Video to Show How Overeating Effects the Stomach
What happens if stomach is not able to hold food?
If the stomach is not able to hold food, three things can happen:
- The stomach can get ruptured
- The food can go up and you can start to vomit
- The food can pushed into small intestine
The chances of stomach getting ruptured are rare, so the food is most likely to go back up in the esophagus or down into the small intestine. When the food goes up it comes out of the system through vomiting. Vomiting is also not common because when we overeat the brain sends strong signals to stop us from overeating. Also, people donât vomit after they overeat is because the stomach muscles get so stretched and weak after overeating that it cannot vomit the excess food. So the food you eat usually remains in your stomach and affect other parts of the body.
Other problems due to overeating
Overeating on regularly not only causes short-term discomfort but can also compromise the long-term health of a person. Some of the problems that people face when they overeat include:
Shortness of Breath
When a person overeats, the stomach muscle gets overstretched and it starts moving towards the lungs and diaphragm. After a large meal, the stomach muscles can expand up to 3 times its normal size which can make it difficult for a person to breathe until the stomach returns to its normal size.
Nausea and Burping
When you overeat not all food you eat does not make it to the stomach immediately. This could bring the food back up in the throat which can cause frequent burping and nausea.
Heartburn
When a person overeats, it becomes difficult for the valve on the top of the stomach to close. This could allow the digestive fluids in the stomach to be pushed back up into the throat which can cause an acidic reaction. Acid reflux can cause severe discomfort and if it continues on a regular basis, it could damage the delicate tissue lining of the throat. At times, the damaged tissue lining could lead to throat cancer.
Tired and Lazy
When a person overeats, the body has to spend more energy to digest the food. Also, the intestine and the stomach will have to work harder to distribute all the nutrients they have received. This leads to an energy drain and you start yawning and feel sleepy.